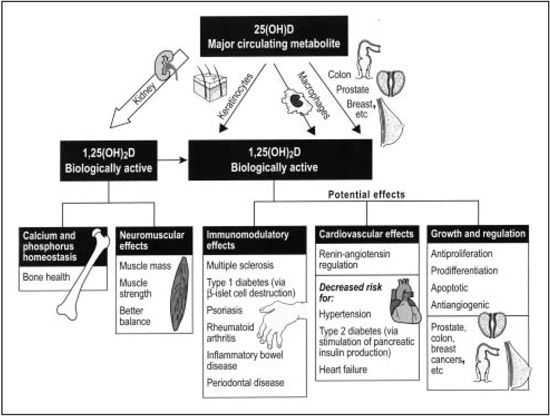
Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin synthesized from cholesterol by the skin where it is exposed to ultra-violet B radiation (sun exposure). Once vitamin D is synthesized it is altered by the liver and kidney into its active form. Small amounts are obtained from dietary sources. Recent research points to a vitamin D deficiency epidemic in the U.S. Sunscreens (to include make-up) with an SPF (sun protection factor) of greater than 8 inhibit the synthesis of vitamin D. Not only is vitamin D necessary to maintain normal calcium levels, but it helps with the maintenance of the neuromuscular system and the immune system. In addition, vitamin D has genetic effects by regulating cell growth and differentiation. Some vitamin D deficiency associated diseases include rickets, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, and cancer. Recently, new research has identified vitamin D playing a role in the prevention of diabetes. Vitamin D is a very safe and effective treatment to use in lieu of the flu shot.
Signs & Symptoms of Deficiency:
- Poor immune function
- bow legs (softening or malformation of the bones)
- Muscle pain
- Muscle weakness
- Poor growth
- Skin lesions (eczema)
- Acne
- Chronic infection
- Sinus infections
Vitamin D has been shown to be beneficial in the following conditions:
- Cancer
- High blood pressure
- Type I and Type II Diabetes
- Osteoporosis
- Rickets
- Osteomalacia
- Autoimmune diseases
- Multiple Sclerosis
Drugs or additives that may deplete or interfere with Vitamin D metabolism:
- Alcohol
- Corticosteroids
- Olestra (a food additive found in many fat free products)
- Mineral oil (when taken consistently in higher doses)
- Cholestyramine
- Colesevelam (Welchol)
- Colestipol
- Statin medications – Although these medications have not been shown to directly decrease vitamin D levels in research studies, they inhibit cholesterol synthesis which could potentially effect vitamin D production.
- Long term therapy with anti-convulsant medications is thought to interfere with the liver and kidneys ability to activate vitamin D.
- Isoniazid and Rifampicin (Antibiotics) are also thought to interfere with the liver and kidneys ability to activate vitamin D.
Laboratory testing for Vitamin D:
- 25 OH-D is the most accurate way to measure this nutrient
- Lymphocyte proliferation assays (Spectracell labs)
Food Sources:
- Sunlight is the best source of natural vitamin D. However; the following foods also contain some vitamin D – Liver, cod liver oil, herring, salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna, eggs, andfortified dairy products.